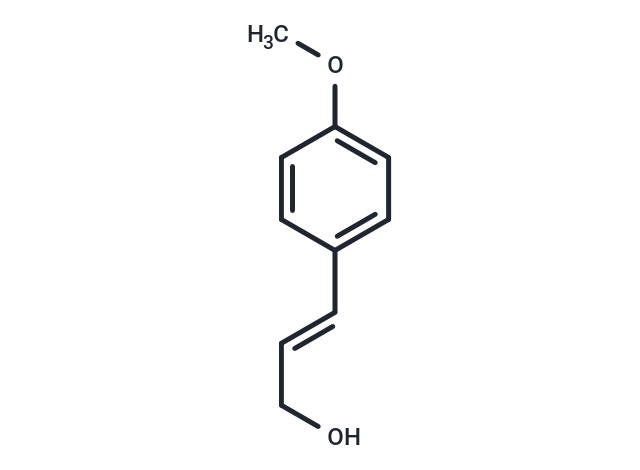
4-Methoxycinnamyl alcohol
CAS No. 53484-50-7
4-Methoxycinnamyl alcohol( —— )
Catalog No. M37755 CAS No. 53484-50-7
4-Methoxycinnamyl alcohol showed toxicity to MCF-7, HeLa and DU145 cancer cell lines with IC50 values of 14.24, 7.82 and 22.10 μg/mL, respectively.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 298 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 473 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 689 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 1040 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1398 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name4-Methoxycinnamyl alcohol
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description4-Methoxycinnamyl alcohol showed toxicity to MCF-7, HeLa and DU145 cancer cell lines with IC50 values of 14.24, 7.82 and 22.10 μg/mL, respectively.
-
Description4-Methoxycinnamyl alcohol showed toxicity to MCF-7, HeLa and DU145 cancer cell lines with IC50 values of 14.24, 7.82 and 22.10 μg/mL, respectively. 4-Methoxycinnamyl alcohol was isolated from Foeniculum vulgare. 4-Methoxycinnamyl alcohol did not show apoptotic effects but showed necrosis after 48 h in a 10 μg/mL DNA fragmentation study.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number53484-50-7
-
Formula Weight164.2
-
Molecular FormulaC10H12O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCOC1=CC=C(\C=C\CO)C=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
6-ROX
6-ROX is a fluorescent oligonucleotide marker and acts as an acceptor molecule coupled to 5-FAM as the donor in FRET imaging with excitation of 568nm and emission of 568nm.
-
Apigenin 7-[rhamnosy...
The leaves of Turpinia arguya Seem.
-
Sodium Danshensu
Danshensu (sodium salt) is sodium salt of danshensu from the widely used Chinese herb Danshen. It can inhibited phenylephrine- and CaCl2-induced vasoconstriction in Ca2+-free medium.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


